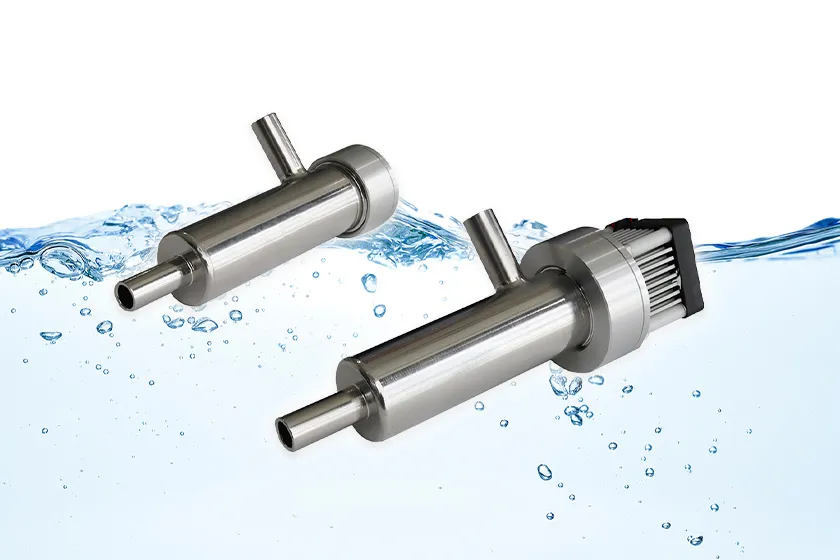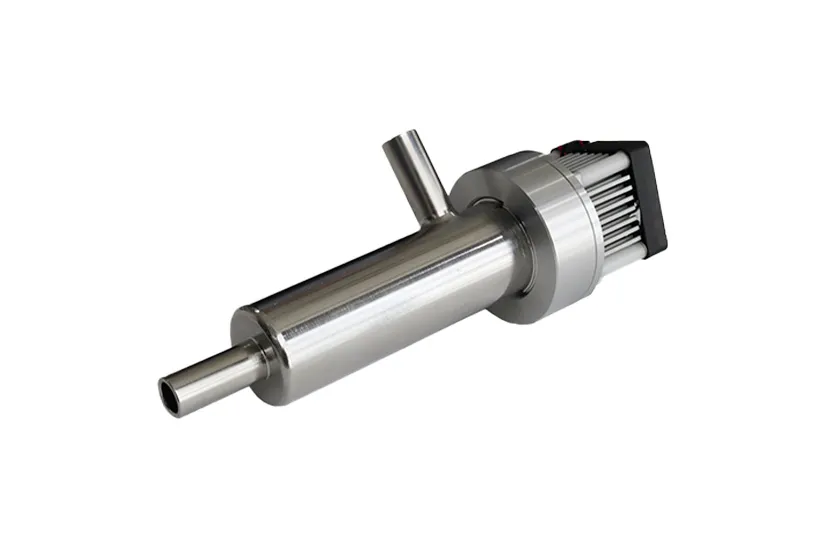
The Disinfection Effect of UV Rays
How UV Effect for Disinfection?
UV disinfection has features that are different to other disinfection methods that use heat or chemicals, and can be used in many different situations.
What are Advantages of UV Disinfection?
-
MERIT 01
There is no need to wipe and clean the area after use as is the case with chemicals.
-
MERIT 02
UV is also effective against microorganisms that are resistant to chlorine, when chlorine disinfection does not work.
-
MERIT 03
This method does not create bacteria that is resistant to UV disinfection.
Precautions for UV Disinfection
- It may cause health problems to humans and living things (acute and chronic ultraviolet radiation induced damage).
- It may cause discoloration and deterioration of such as organic materials, typically resin and plastic-based material.
- Places in shadow or where light does not reach cannot be disinfected using this method.
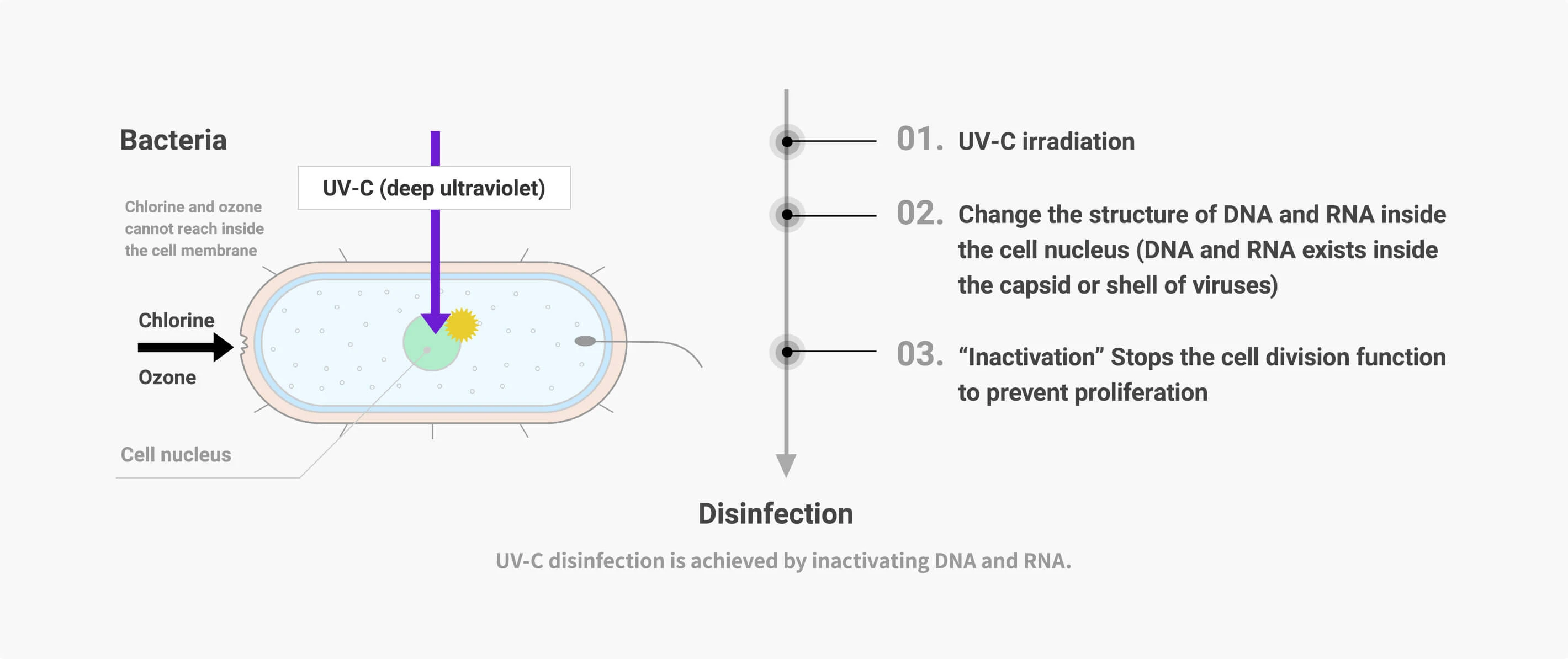
How Does UV-C Disinfection Proceed?
Bacteria and viruses proliferate by cell division based on genetic information to cause infection and illness. DNA and RNA holds the genetic information necessary for this proliferation to occur. Irradiating with UV-C changes the helix structure of DNA and RNA of held by bacteria and viruses, which can inactivate these bacteria and viruses resulting in reducing their proliferation.
Fig.1: UV-C Disinfection Process
Disinfection Effect Varies Depending on UV Wavelength
The disinfection effect on DNA and RNA of bacteria and viruses depends a lot on the UV wavelength. Within the ultraviolet range of UV-A, UV-B and UV-C, UV-C with the shortest wavelength can provide the greatest performance to inactivate bacteria and viruses. Its effect is over 1,000 times greater than UV-A and over 50 times greater than UV-B.
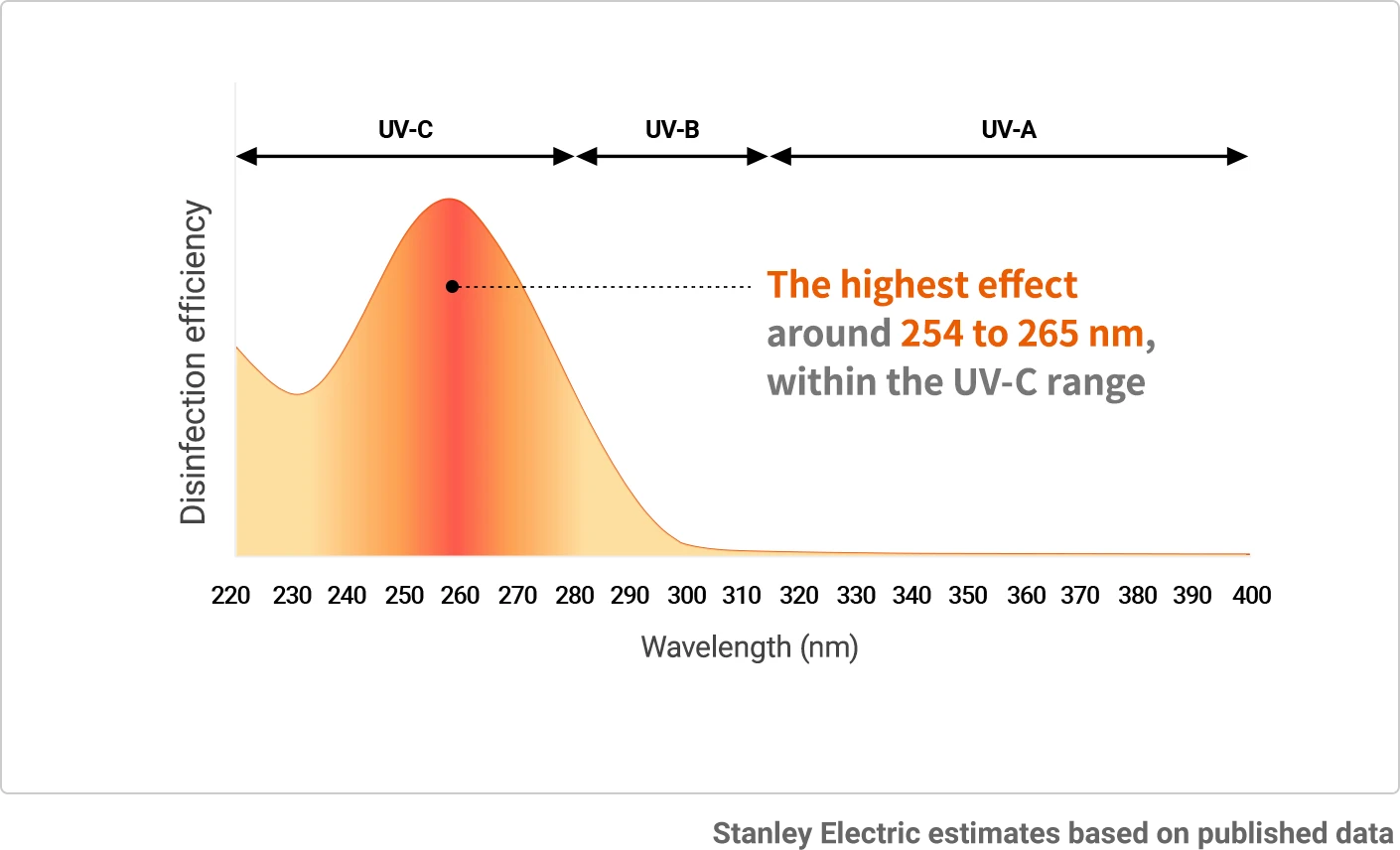
Furthermore, from Fig.3 we can see that a wavelength of around 265 nm from among UV-C wavelengths (100 nm to 280 nm) provides the highest inactivation efficiency. Stanley Electric develops and manufactures UV-C LEDs that generate light with a peak wavelength of 265 nm, which has the highest disinfection effect.
Comparison of Disinfection Performance by UV Wavelength
Fig.2: Comparison of Disinfection Performance by UV Wavelength
(When the disinfection effect of 265nm is set at 100%)
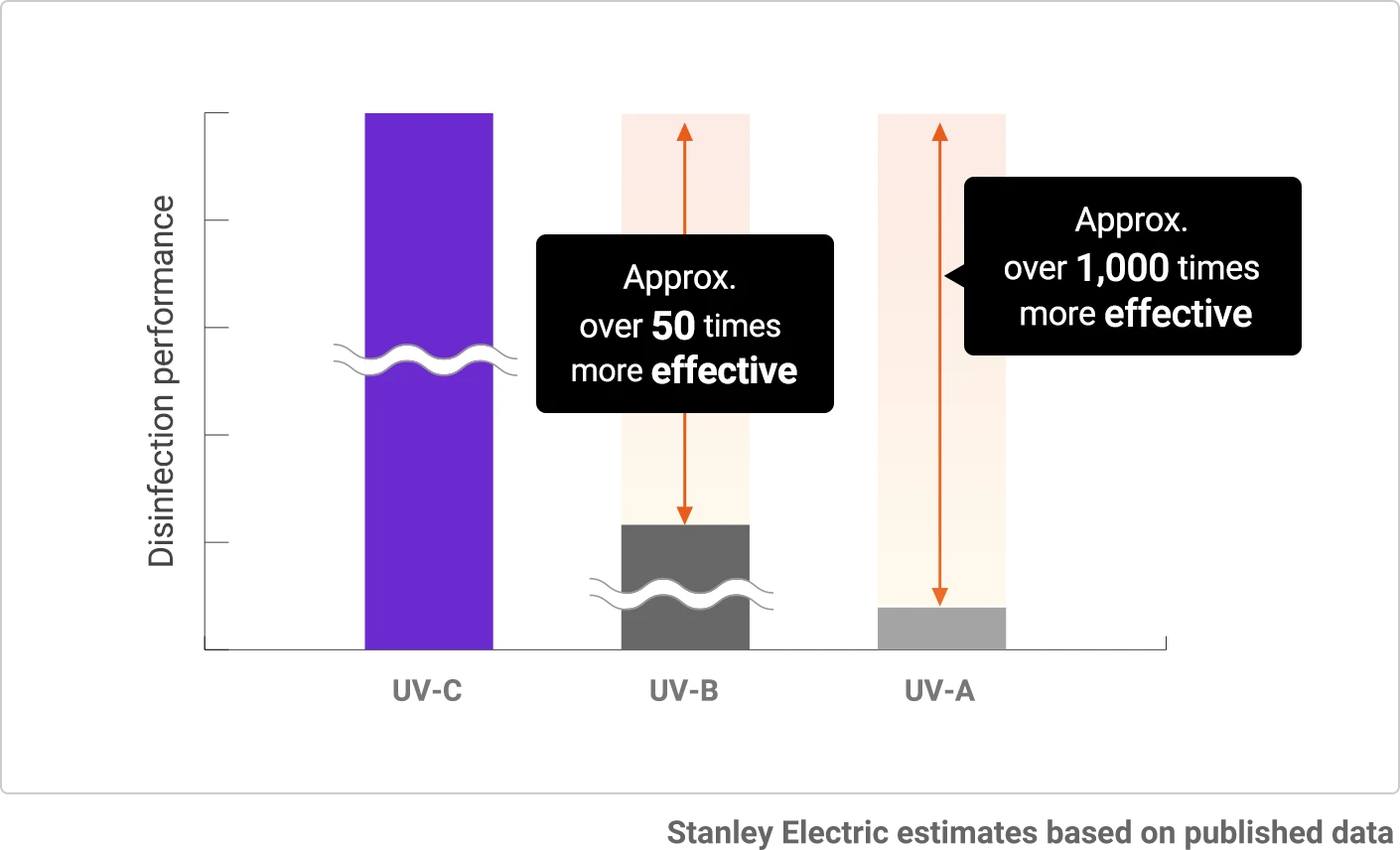
Fig.3: Inactivation Efficiency by Wavelength
How The Disinfection Effect is Calculated?
The required irradiation amount and conditions by ultraviolet varies depending on the targeted type of bacteria, virus, and other microorganisms. In general, the disinfection effect is determined by totaling (the cumulative light amount or ultraviolet dose) the light strength (intensity) and the time UV light is shone onto the object (irradiation time). The longer irradiation time, the more the cumulative light amount increases, resulting in a greater disinfection effect. Conversely, a high output ultraviolet intensity is required when disinfecting is required for a short time.
How The Cumulative Light Amount is Calculated?
Example: When an ultraviolet dose of 40 mJ/cm2 is required to disinfect 99.99% of bacteria A
Intensity
(2mW/cm2)
×
Intensity time
(20 seconds)
=
Cumulative light amount
(40mJ/cm2)
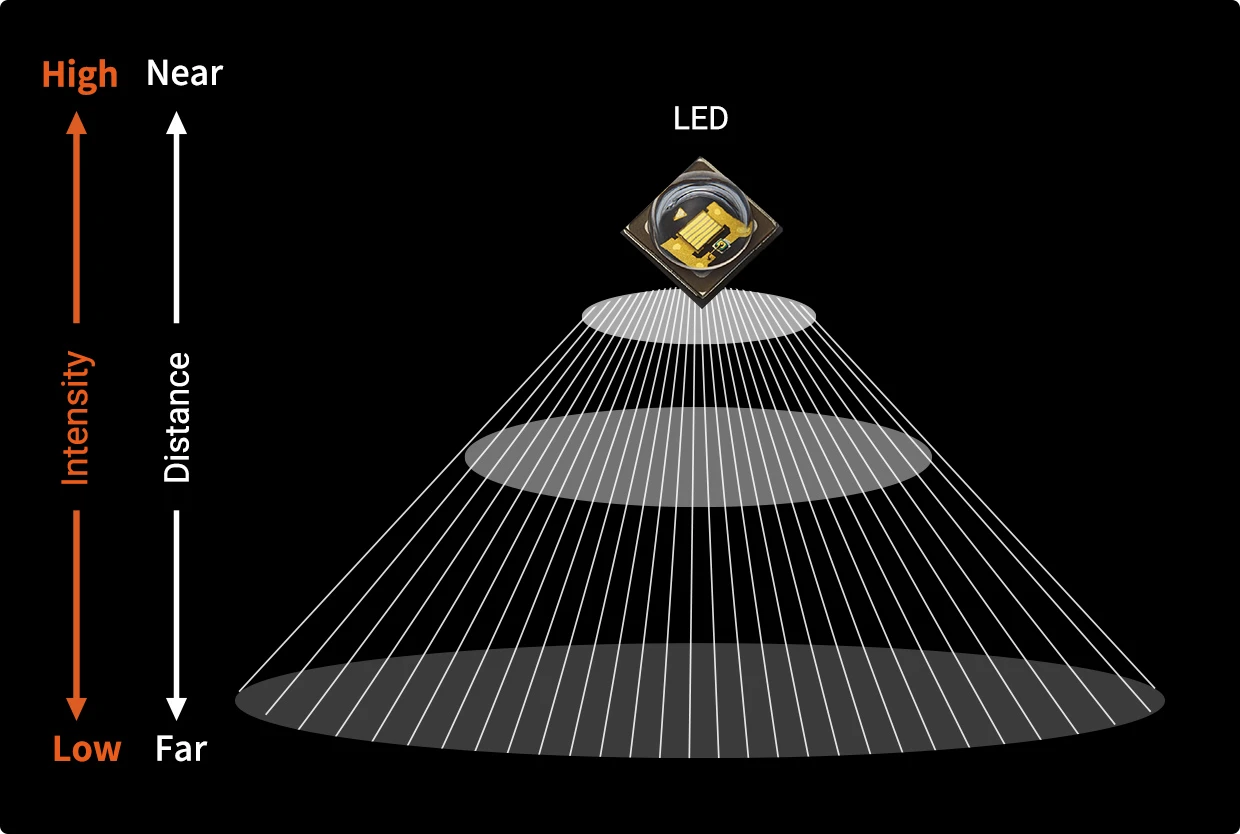
Intensity Depending on The Distance
The intensity changes depending on the distance to the object. In general, the intensity falls the further the distance to the object from the light source. And intensity increases the closer to the light source axis, and intensity decreases the greater the displacement from the axis.